Anaplan Best Practices
At ACCTER, we are committed to continuous learning to provide you and your business with the best possible solutions. Over the course of various projects, we’ve tackled challenges by combining our expertise with a set of golden rules. Discover the most common pitfalls new model builders face and learn how to avoid them by implementing the following best practices.
- Keys & Lists: The Foundation of Efficient Models
A well-structured foundation is critical to an efficient Anaplan model. Try to avoid using Date as part of a unique key. Adding dates to the keys can lead to performance lags and unnecessary model size increases. Instead, create a module to store the attributes or properties and another module dimensionalized by Transactions and Time. Import to Transaction module and create a summary module to sum against transaction module.
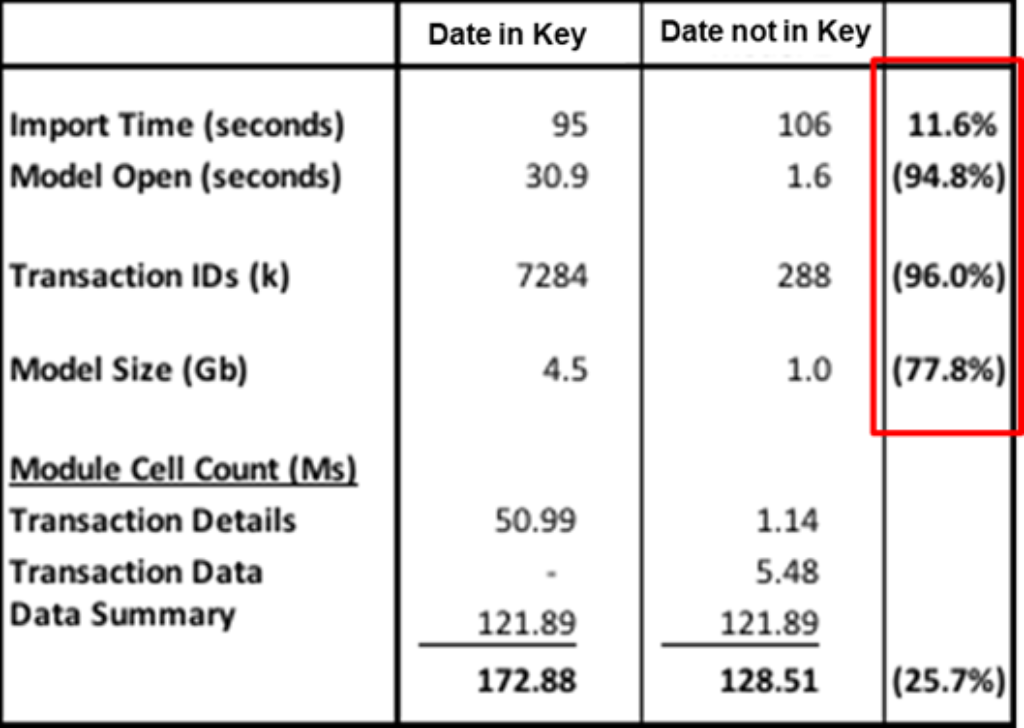
Next, builders must leverage Source System Codes. If your source system already provides unique identifiers, use them. This reduces processing overhead and ensures alignment across systems. Finally, optimize you Lists. Do so by separating subset lists to improve focus and usability and removing unnecessary top-level hierarchies, which can contribute to model bloat. Try to centralize Properties in System Modules. Replace excessive list properties with centralized system modules, enabling more flexibility and faster recalculations. Furthermore, it can enhance accessibility for all team model builders and simplify maintenance.
- Module Design: Building for Clarity and Speed
Modules are the heart of your Anaplan model, and their design significantly impacts performance. During our build we try to maximize efficiency by considering some key rules. Try to streamline repetitive calculations. Housing recurring calculations in system modules not only improves efficiency but ensures consistency across the model. Think critically about the number of dimensions, time ranges and line items. Include only essential dimensions in modules to reduce sparsity and improve performance. Be deliberate about setting time ranges and filters to avoid unnecessary data. Further, if a module exceeds 50 line items, consider breaking it into smaller, focused modules. This is especially critical when using subsidiary views, which can quickly complicate calculations.
- Performance and size Optimization: Fast, Lean, and Effective
Performance optimization is an ongoing effort. Small tweaks can lead to significant gains in speed and efficiency. During several of our projects we noticed that space could easily be saved when reviewing and adjusting summary methods to avoid unnecessary summaries. Further, builders sometimes forget to take in mind that headers can be set to ‘No Data’ which will avoid additional calculations.
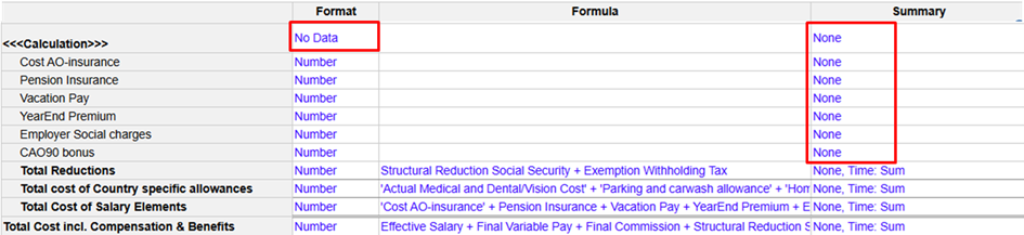
Next, as Anaplan is optimized for numbers and Booleans, check for overuse of text formatted line items as they take more memory than most other model components and do not perform as well as other data types.

Formatting and summaries are not the only pitfalls. Model builders frequently overlook the need to adapt their filter settings in saved views after making changes. Incorrect filtering in saved views reduces performance. For example, if three line items are needed, but 25 line items are defined, performance will be impacted. Filters should be set up using Boolean values and have only one line item filtering each dimension. If multiple filtering line items are required, consider consolidating them into a single line item.
Further, builders can be tempted to use a number instead of a Boolean for an equality test. However, this must be avoided as numbers take 8 times the space of Boolean and the equality test takes more time. Therefor, only use numbers for logical conditions if Booleans cannot live up to the task.
Often forgotten, however not less important: consistent dimension ordering. Always follow a standard order for dimensions across modules to speed up calculations. Maintaining a consistent order of dimensions is crucial for improving your model's performance. This applies to both modules and individual line items. Why is dimension order important? Anaplan assigns index numbers to each cell where dimensions intersect, which it uses to perform calculations. A consistent dimension order ensures these calculations are executed more efficiently.
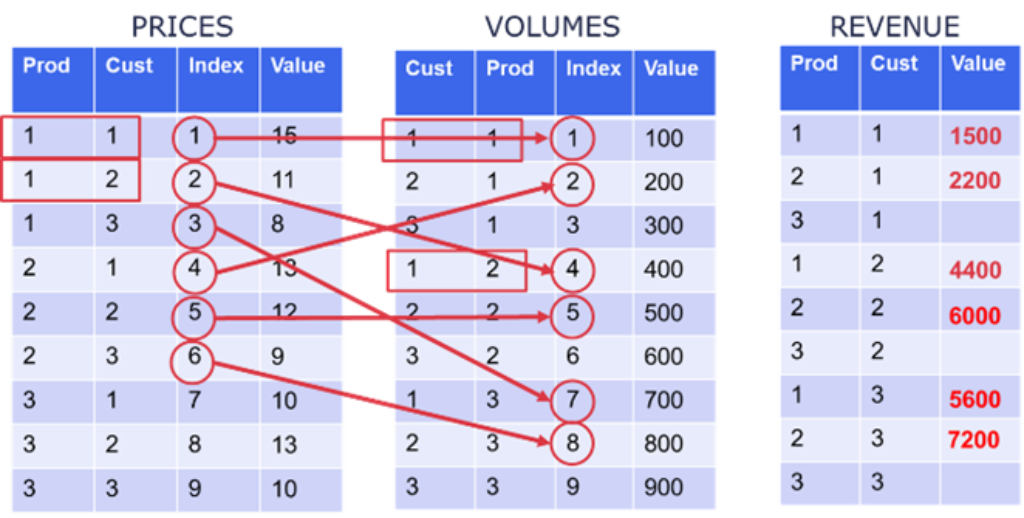
- Formulas and Logic: a few quick tips and tricks
Complex formulas can slow down your model and make troubleshooting a nightmare. Here are some quick tips for optimizing your logic. At all cost avoid SUM + LOOKUP combinations by putting them into different modules and line items. Including these functions in the same formula often leads to large calculations, particularly when time is a dimension or when the source and target structures differ significantly. Next, when using IF statements, place the most likely condition first. Applying this ‘Early Exit Strategy’ minimizes unnecessary processing for less likely scenarios. Further, replace Hardcoding with System Modules. Hardcoding values or using SELECT functions can limit flexibility and introduce maintenance headaches. Instead, store assumptions in system modules and use LOOKUP formulas to reference them dynamically. Finally, remember that formulas should be easy to audit. Simplify your formulas by avoiding lengthy IF statements and complex dependency chains, as these can hinder both auditability and performance. Instead, break formulas and chains into smaller, more manageable components.


